The AfriCarbon
Concept
Restoration of desertified thicket landscapes revives ecosystems and rural economies by generating carbon credits and financial returns on investment.
The desertification of the Eastern Cape
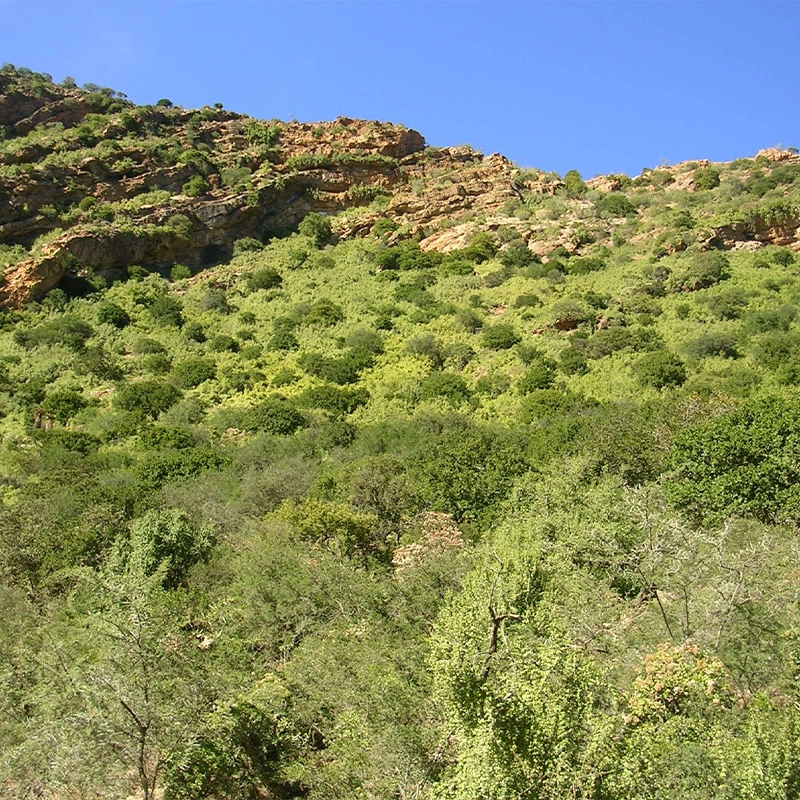
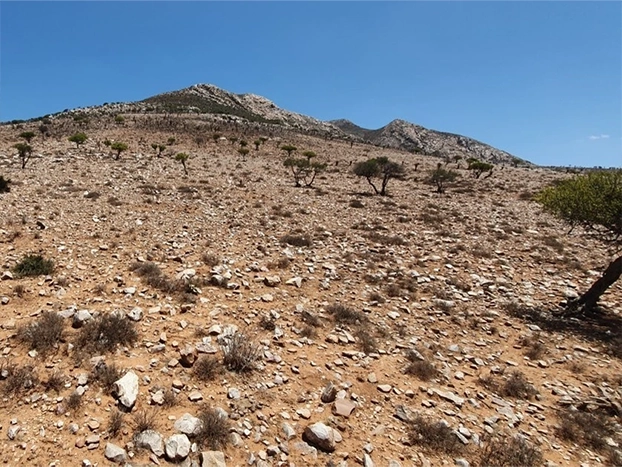
More than 1 million hectares of thicket vegetation in the Eastern Cape, South Africa have been degraded by goat farming over the past century. The change in the landscape is startling: a dense, virtually impenetrable forest is transformed by the goats into an open, desert-like landscape with a smattering of intensively pruned trees.
This is desertification in its most extreme form. Soils are exposed to the impact of raindrops and rapidly erode, with entire topsoil horizons ending up in rivers and dams. The animals and plants of the forested environment are largely absent. The few trees that remain are the “living dead” because their seedlings cannot survive in the baking sun. The desertified landscape is a mere shadow of its former self. In wet years this human-induced desert is transformed into a lush green pasture of annual grasses and shrubs, and livestock thrives. But in dry years (which are common in the Eastern Cape), the land’s surface remains brown and pickings are slim for herbivores.
Rolling back the desert
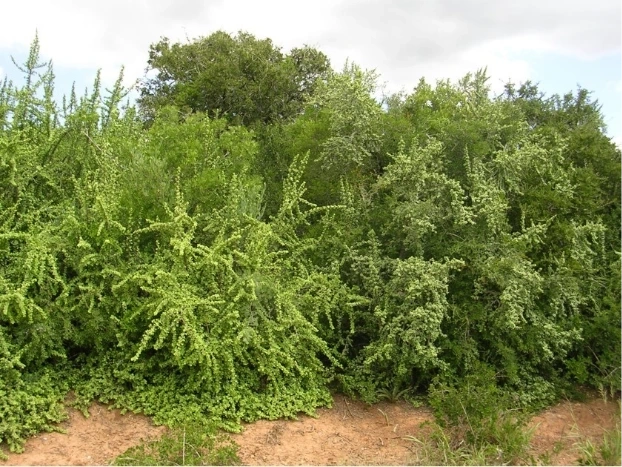
Fortunately there is a practical way of rolling back the desert using the remarkable succulent tree Portulacaria afra (spekboom). This plant grows in abundance in many thicket types and grows to a height of 4 meters and more in certain areas. Furthermore, it can be grown from cuttings planted in either wet or dry soils. Farmers across the Eastern Cape have used spekboom cuttings to great effect for creating dense hedges in their gardens and in a few cases restoring large areas of the goat-degraded landscapes.
Using spekboom to initiate natural recovery
Spekboom is the centre-piece of AfriCarbon’s vision. Planting spekboom cuttings on a large scale, over tens or even hundreds of thousands of hectares, in goat-degraded thicket results in the rebuilding of carbon-rich topsoils. The considerable amount of carbon captured in the plant and the soils can be sold as carbon credits on local or international markets, making the planting operation not only financially viable, but more profitable than present agricultural uses for the land. Indeed, the more than 1 million hectares of degraded thicket represent a significant business opportunity for spekboom carbon farmers. As well as benefitting financially, by returning the dominant indigenous plant in the region (i.e. spekboom,) the carbon farmer is creating a cooler, more benign environment for other thicket plant species to establish. Over decades, the thicket and its fauna will return.
The knock-on benefits of thicket restoration
Thicket in its natural or restored state has significant benefits.
Black rhino, elephant and other game thrive in this vegetation and ecotourism opportunities would abound with tens of thousands of contiguous hectares of spekboom-rich thicket in place.
Bees are also highly productive insects in intact thicket, and beekeeping is likely to be a viable business in the restored landscapes.
Even livestock can play a role in the new restoration economy that will emerge from landscapes restored with spekboom cuttings, if kept at stocking levels which enable the cuttings to flourish.
Planting spekboom is labour intensive and consequently carbon farmers in this vision will be major employers in the Eastern Cape, providing a much-needed stimulus to the depressed rural economy of the region.
Carbon credit return
Landscapes restored with spekboom cuttings can potentially generate more than 10 carbon credits per hectare per year over a 30-year period. The cost of planting spekboom cuttings and transaction costs involved in generating carbon credits (e.g. monitoring and evaluation, validation, certification, project development and baseline development) can be considerable, but income from carbon credits more than offsets these costs over the project lifetime. AfriCarbon has undertaken detailed financial modeling of a range of restoration scenarios involving different soil types, distances from local towns, and distances from spekboom sources. These scenarios can be discussed in greater detail with stakeholders interested in participating and investing in restoration projects.
Spekboom
How does Spekboom defy the desert odds?
The potential financial returns from restoration with spekboom cuttings
Before
After






